遠(yuǎn)程-安全日志帳戶登錄失敗(審核失敗)-針對ntlmssp攻擊的本機安全設(shè)置(登錄進(jìn)程:NtLmSsp)
廣告:
主題:
安全 ID: NULL SID
帳戶名: -
帳戶域: -
登錄 ID: 0x0
登錄類型: 3
登錄失敗的帳戶:
安全 ID: NULL SID
帳戶名: TEST
帳戶域:
失敗信息:
失敗原因: 未知用戶名或密碼錯誤。
狀態(tài): 0xc000006d
子狀態(tài): 0xc0000064
進(jìn)程信息:
調(diào)用方進(jìn)程 ID: 0x0
調(diào)用方進(jìn)程名: -
網(wǎng)絡(luò)信息:
工作站名:
源網(wǎng)絡(luò)地址: -
源端口: -
詳細(xì)身份驗證信息:
登錄進(jìn)程: NtLmSsp
身份驗證數(shù)據(jù)包: NTLM
傳遞服務(wù): -
數(shù)據(jù)包名(僅限 NTLM): -
密鑰長度: 0
登錄請求失敗時在嘗試訪問的計算機上生成此事件。
“主題”字段指明本地系統(tǒng)上請求登錄的帳戶。這通常是一個服務(wù)(例如 Server 服務(wù))或本地進(jìn)程(例如 Winlogon.exe 或 Services.exe)。
“登錄類型”字段指明發(fā)生的登錄的種類。最常見的類型是 2 (交互式)和 3 (網(wǎng)絡(luò))。
“進(jìn)程信息”字段表明系統(tǒng)上的哪個帳戶和進(jìn)程請求了登錄。
“網(wǎng)絡(luò)信息”字段指明遠(yuǎn)程登錄請求來自哪里。“工作站名”并非總是可用,而且在某些情況下可能會留為空白。
“身份驗證信息”字段提供關(guān)于此特定登錄請求的詳細(xì)信息。
-“傳遞服務(wù)”指明哪些直接服務(wù)參與了此登錄請求。
-“數(shù)據(jù)包名”指明在 NTLM 協(xié)議之間使用了哪些子協(xié)議。
事件id:4625
來源:Microsoft Windows security auditing.
解決方法:管理工具本地安全策略進(jìn)行NTLM策略控制,徹底阻止LM響應(yīng)(NTLM是NT LAN Manager的縮寫,即NT LAN管理器)
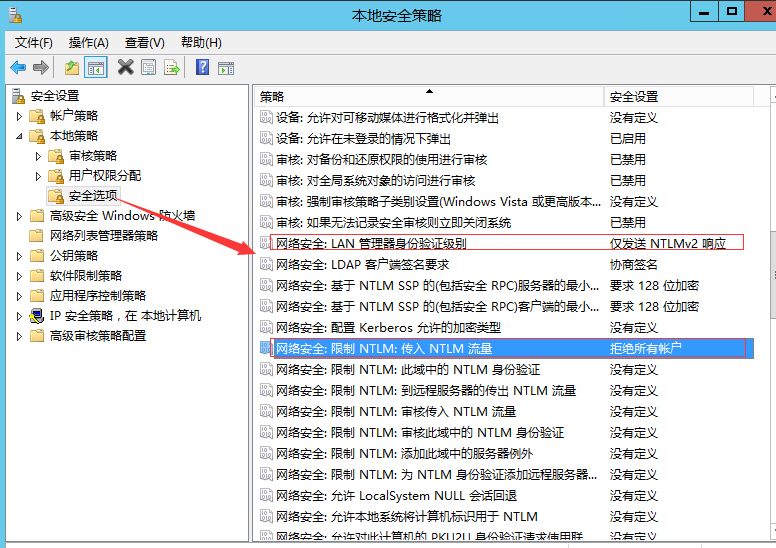
1 本地策略---安全選項----網(wǎng)絡(luò)安全:LAN管理器身份驗證級別 僅發(fā)送NtLMv2響應(yīng) 拒絕 LM響應(yīng) 和 NTLM。
2 本地策略---安全選項----網(wǎng)絡(luò)安全:限制 NTLM:傳入NTLM流量 拒絕所有賬戶 (添加此步可能導(dǎo)致不能遠(yuǎn)程登錄,但可在云控制臺登錄)
或者在安全組遠(yuǎn)程端口如:3389中,源ip中只充許指定的ip訪問也可阻止此類攻擊。
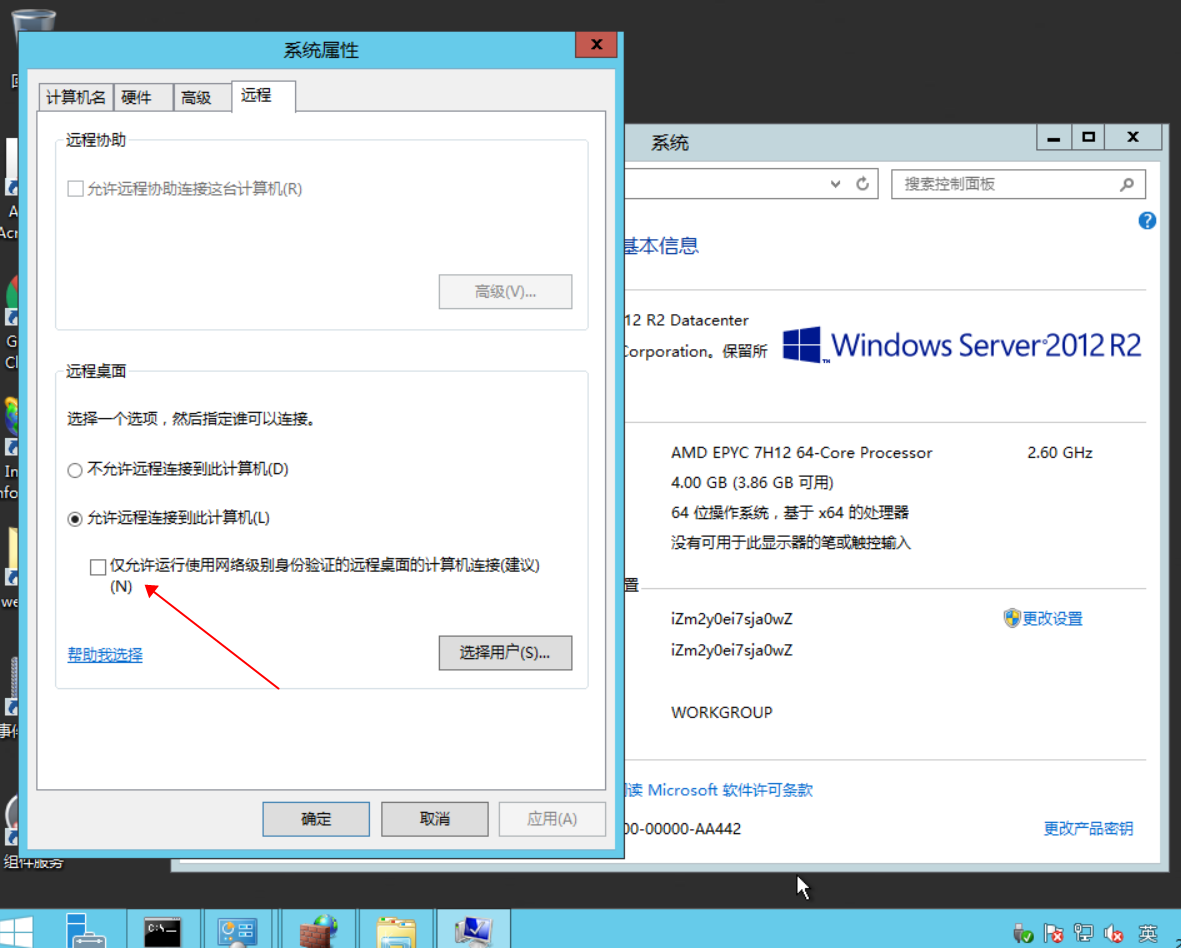
如果提示:由于credssp加密數(shù)據(jù)庫修正,不能遠(yuǎn)程登錄,請在服務(wù)器按下面操作:
此安全設(shè)置確定網(wǎng)絡(luò)登錄使用的質(zhì)詢/響應(yīng)身份驗證協(xié)議。此選項會影響客戶端使用的身份驗證協(xié)議的等級、協(xié)商的會話安全的等級以及服務(wù)器接受的身份驗證的等級,其設(shè)置值如下:
發(fā)送 LM NTLM 響應(yīng): 客戶端使用 LM 和 NTLM 身份驗證,而決不會使用 NTLMv2 會話安全;域控制器接受 LM、NTLM 和 NTLMv2 身份驗證。
發(fā)送 LM & NTLM – 如果協(xié)商一致,則使用 NTLMv2 會話安全: 客戶端使用 LM 和 NTLM 身份驗證,并且在服務(wù)器支持時使用 NTLMv2 會話安全;域控制器接受 LM、NTLM 和 NTLMv2 身份驗證。
僅發(fā)送 NTLM 響應(yīng): 客戶端僅使用 NTLM 身份驗證,并且在服務(wù)器支持時使用 NTLMv2 會話安全;域控制器接受 LM、NTLM 和 NTLMv2 身份驗證。
僅發(fā)送 NTLMv2 響應(yīng): 客戶端僅使用 NTLMv2 身份驗證,并且在服務(wù)器支持時使用 NTLMv2 會話安全;域控制器接受 LM、NTLM 和 NTLMv2 身份驗證。
僅發(fā)送 NTLMv2 響應(yīng)\拒絕 LM: 客戶端僅使用 NTLMv2 身份驗證,并且在服務(wù)器支持時使用 NTLMv2 會話安全;域控制器拒絕 LM (僅接受 NTLM 和 NTLMv2 身份驗證)。
僅發(fā)送 NTLMv2 響應(yīng)\拒絕 LM & NTLM: 客戶端僅使用 NTLMv2 身份驗證,并且在服務(wù)器支持時使用 NTLMv2 會話安全;域控制器拒絕 LM 和 NTLM (僅接受 NTLMv2 身份驗證)。
默認(rèn)值:
Windows 2000 以及 Windows XP: 發(fā)送 LM & NTLM 響應(yīng)
Windows Server 2003: 僅發(fā)送 NTLM 響應(yīng)
Windows Vista、Windows Server 2008、Windows 7 以及 Windows Server 2008 R2及以上: 僅發(fā)送 NTLMv2 響應(yīng)
NTLMSSP, whose authentication service identifier is RPC_C_AUTHN_WINNT, is a security support provider that is available on all versions of DCOM. It uses the NTLM protocol for authentication. NTLM never actually transmits the user's password to the server during authentication. Therefore, the server cannot use the password during impersonation to access network resources that the user would have access to. Only local resources can be accessed.
NTLM works both locally and across computers. That is, if the client and server are on different computers, NTLM can still make sure the client is who it claims to be.
With NTLM, the client's identity is represented by a domain name, user name, and a password or token. When a server calls CoQueryClientBlanket, the client's domain name and user name are returned. However, when a server calls CoImpersonateClient, the client's token is returned. If there is no trust relationship between client and server and if the server has a local account with the same name and password as the client, that account will be used to represent the client.
NTLM supports mutual authentication cross-thread and cross-process (locally only). If the client specifies the principal name of the server in the form domain\user in a call to IClientSecurity::SetBlanket, the server's identity must match that principal name or the call will fail. If the client specifies NULL, the server's identity will not be checked.
NTLM additionally supports the delegate impersonation level cross-thread and cross-process (locally only).
廣告:


